Tree taxonomic classification workflow
Workflow details in development
After identifying the locations and sizes of individual trees, the next step is to identify each tree taxonomically. The Geograypher tool enables powerful workflows for training and deploying computer vision models for tree taxonomic identification and other tasks, taking advantage of the fact that each tree generally appears in numerous drone images from different angles. The tool enables projection of geospatial data (e.g., tree species labels) onto raw drone images, and vice versa, taking advantage of the fact that if we know the precise position of the drone camera and the parameters of its lens, we can translate any given pixel in a drone image into a ray through 3D geospatial space.
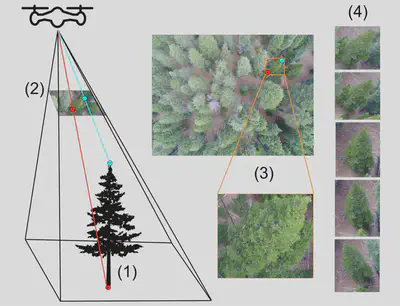
Using Geograypher, a geospatial map (e.g. of species identities) can be projected onto the raw drone images and used (for example) for training a computer vision algorithm to identify tree species (or detect trees) using the raw drone images. Similarly, if one has tree species identities annotated on the raw drone images (e.g., the result of running computer vision inference on the images), Geograypher can project these annotations onto the geospatial layers (e.g. orthomosaic) for mapping purposes.